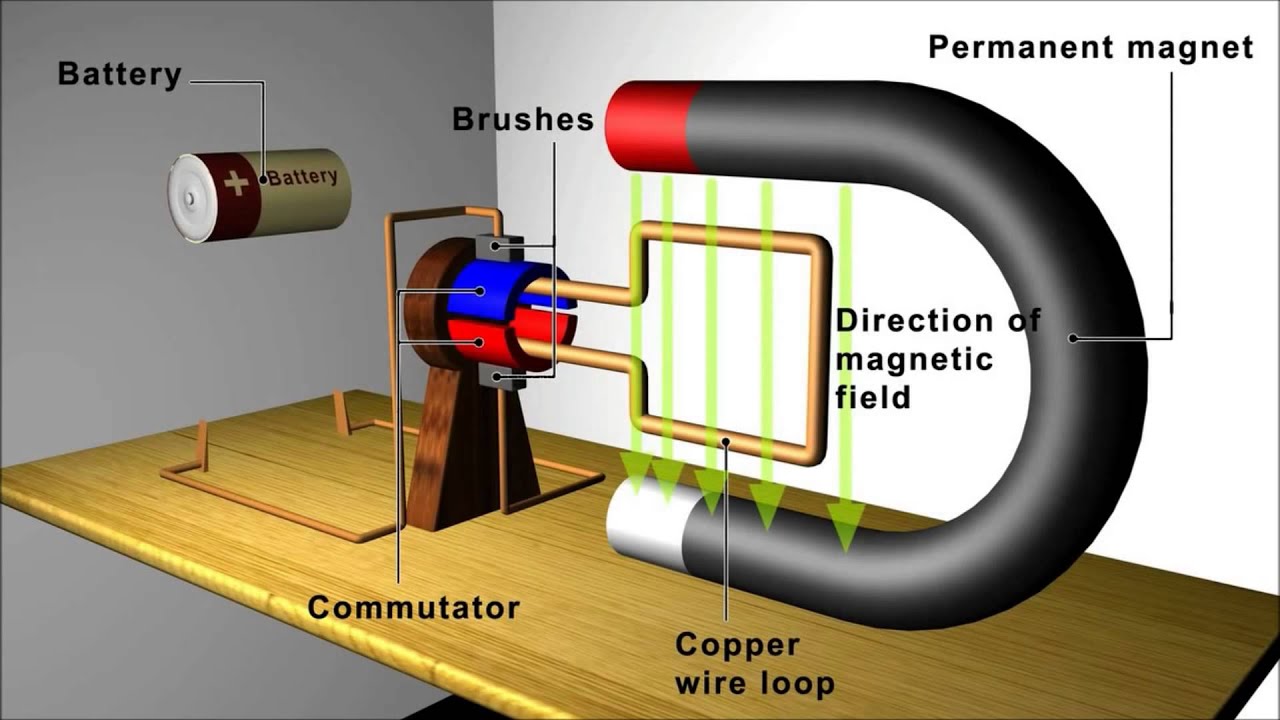
Components of an Electric Motor
Briefly explain how an electric motor works – An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It consists of two main components: the stator and the rotor.
Stator and Rotor
The stator is the stationary part of the motor, while the rotor is the rotating part. The stator contains a set of electromagnets that create a magnetic field. The rotor contains a set of conductors that are connected to an electrical source.
When an electric current flows through the conductors, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field of the stator. This interaction creates torque, which causes the rotor to rotate.
Armature and Field Windings
The armature windings are the conductors that are connected to the electrical source. The field windings are the electromagnets that create the magnetic field in the stator. The armature windings and field windings are connected in a specific way to create the desired magnetic field interaction.
Commutator or Slip Rings
The commutator or slip rings are used to connect the armature windings to the electrical source. The commutator is a mechanical switch that reverses the direction of the current flow through the armature windings. This is necessary to create a continuous rotating motion.
Slip rings are used in AC motors, where the current flow does not need to be reversed.
Principle of Operation
The principle of operation of an electric motor is based on electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor.
Electromagnetic Induction
When a magnetic field changes, it induces an electric current in a conductor. The direction of the current flow depends on the direction of the magnetic field change. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
Interaction of Magnetic Fields, Briefly explain how an electric motor works
In an electric motor, the stator and rotor magnetic fields interact to create torque. The stator magnetic field is created by the field windings. The rotor magnetic field is created by the armature windings. When the stator magnetic field changes, it induces an electric current in the armature windings.
This current flow creates a magnetic field in the rotor, which interacts with the stator magnetic field to create torque.
Types of Electric Motors
There are many different types of electric motors, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
DC Motors
DC motors are powered by a direct current (DC) source. They are typically used in applications where variable speed is required, such as electric vehicles and industrial machinery.
AC Motors
AC motors are powered by an alternating current (AC) source. They are typically used in applications where constant speed is required, such as appliances and power tools.
Brushless Motors
Brushless motors are a type of DC motor that uses electronic commutation instead of a mechanical commutator. They are more efficient and reliable than brushed motors, and they are often used in high-performance applications, such as drones and electric vehicles.
Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are a type of DC motor that can be controlled to move in precise increments. They are often used in applications where precise positioning is required, such as robotics and medical devices.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are used in a wide range of applications, from small appliances to large industrial machinery.
Industrial Applications
Electric motors are used to power a variety of industrial machinery, such as conveyors, pumps, and compressors. They are also used in robotics and automation systems.
Consumer Applications
Electric motors are used in a variety of consumer products, such as appliances, power tools, and electric vehicles. They are also used in toys, medical devices, and other electronic devices.
Transportation Applications
Electric motors are used to power electric vehicles, such as cars, buses, and trains. They are also used in hybrid vehicles, which combine an electric motor with a gasoline engine.
Closing Notes
Our exploration concludes with a comprehensive overview of the various types of electric motors, each tailored to specific applications. We examine the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of different motor types, including DC motors, AC motors, synchronous motors, and induction motors.
Finally, we showcase the wide-ranging applications of electric motors, from powering industrial machinery and household appliances to propelling electric vehicles and enabling advanced robotics. Electric motors stand as a testament to human ingenuity, transforming electrical energy into mechanical motion that drives countless aspects of our modern world.
Answers to Common Questions: Briefly Explain How An Electric Motor Works
What is the basic principle behind the operation of an electric motor?
Electric motors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor. This current creates a force that interacts with the motor’s magnetic field, resulting in torque and rotation.
What are the key components of an electric motor?
The main components of an electric motor include the stator, rotor, armature, field windings, commutator or slip rings, and brushes. The stator and rotor are electromagnets that create the magnetic fields, while the armature and field windings conduct the electric current.
What are the different types of electric motors?
There are various types of electric motors, including DC motors, AC motors, synchronous motors, and induction motors. Each type has unique characteristics and is suited for specific applications.