Prepare to be electrified as we delve into the captivating world of induction motors! These versatile workhorses power countless applications, and in this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover the secrets of what an induction motor works with. From the electrical supply that energizes it to the magnetic field that drives it, we’ll explore every aspect of this fascinating technology.
Induction motors are used in a wide range of applications, from powering conveyor belts to driving fans. They are popular because they are relatively simple to build and maintain. Just like an employee receives 2 vacation days for every month worked , induction motors require regular maintenance to ensure they operate at peak efficiency.
Regular cleaning and lubrication can extend the life of an induction motor and keep it running smoothly.
Induction motors are the unsung heroes of modern society, quietly powering everything from household appliances to industrial machinery. Understanding how they work is not just about technical knowledge; it’s about appreciating the intricate interplay of electricity, magnetism, and motion.
Induction Motor
An induction motor is a type of electric motor that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Induction motors are widely used in industrial and commercial applications, and they are known for their reliability, efficiency, and low maintenance requirements.
An induction motor works with a rotating magnetic field that induces current in the rotor, creating torque. A similar principle applies to an aggressive working capital policy, which involves maintaining low inventory levels and short payment terms . This strategy frees up cash flow for investment and growth, just as an induction motor’s magnetic field drives the rotor to generate motion.
Electrical Supply
Induction motors require an electrical supply to operate. The voltage, current, and frequency of the electrical supply must be compatible with the motor’s design. The most common type of electrical supply for induction motors is a three-phase alternating current (AC) supply.
An induction motor works with alternating current, which is the type of electricity that flows through your home. This makes induction motors ideal for use in a variety of applications, from fans and pumps to conveyor belts and industrial machinery.
If you’re looking for an even better place to work , consider a company that uses induction motors in its products. Induction motors are reliable, efficient, and affordable, making them a great choice for businesses of all sizes.
However, induction motors can also be operated on single-phase AC or DC supplies.
Induction motors work with a spinning magnetic field, which interacts with the motor’s rotor to produce torque. An analysis of working capital management results across industries can help you understand how to optimize your company’s cash flow and profitability. Induction motors are used in a wide variety of applications, from small appliances to large industrial machinery.
- Voltage:The voltage of the electrical supply must match the voltage rating of the motor.
- Current:The current drawn by the motor will vary depending on the load. The electrical supply must be able to provide sufficient current to meet the motor’s maximum load requirements.
- Frequency:The frequency of the electrical supply must match the frequency rating of the motor. The frequency of the electrical supply will determine the speed of the motor.
Magnetic Field
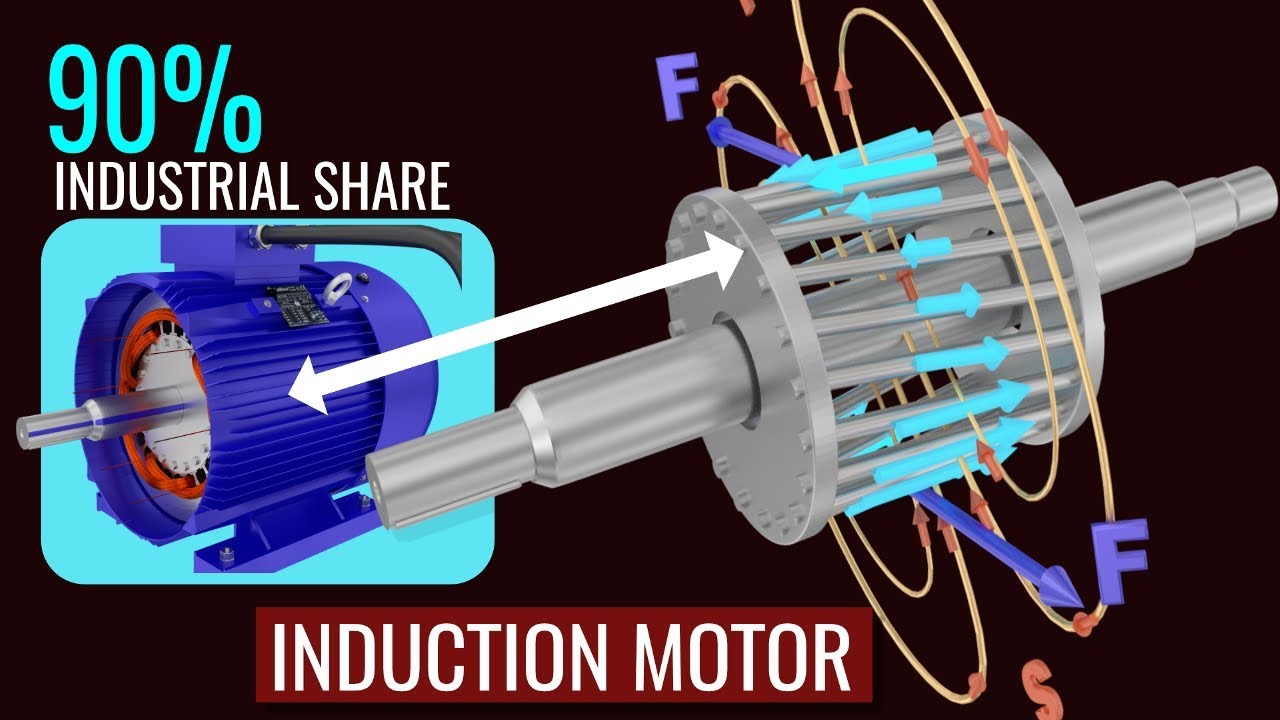
Induction motors create a rotating magnetic field using two sets of windings: the stator windings and the rotor windings. The stator windings are located on the outer frame of the motor, while the rotor windings are located on the inner rotor.
An induction motor works with alternating current (AC), and one example of working capital is an example of working capital . It is a financial measure that shows the difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities, and it is used to assess a company’s short-term financial health.
An induction motor works with alternating current (AC), and the amount of working capital a company has can impact its ability to operate effectively.
When the stator windings are energized, they create a magnetic field that rotates around the stator. This rotating magnetic field induces a current in the rotor windings, which in turn creates a magnetic field around the rotor. The interaction between the stator and rotor magnetic fields causes the rotor to rotate.
Rotor Construction
The rotor of an induction motor is typically made of aluminum or copper. The rotor windings are embedded in slots in the rotor core. The rotor core is made of laminated steel to reduce eddy current losses. There are two main types of rotor designs: squirrel-cage rotors and wound-rotor rotors.
An induction motor works with an alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, which in turn induces an electric current in the motor’s rotor. Similarly, after an abortion, it’s crucial to understand when it’s safe to resume physical activity.
If you’re wondering after an abortion when can i work out , it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate time frame for you. Continuing, an induction motor works with alternating current, while a DC motor works with direct current.
- Squirrel-cage rotorsare the most common type of rotor design. They are made of a series of copper or aluminum bars that are connected together at the ends. Squirrel-cage rotors are simple to manufacture and maintain.
- Wound-rotor rotorsare made of a series of coils that are connected together. Wound-rotor rotors provide better speed control than squirrel-cage rotors, but they are more expensive to manufacture and maintain.
Slip
Slip is the difference between the speed of the rotating magnetic field and the speed of the rotor. Slip is expressed as a percentage of the synchronous speed, which is the speed of the rotating magnetic field. Slip is caused by the load on the motor.
As the load increases, the slip increases. Slip is also affected by the design of the motor. Motors with a high slip have a higher starting torque than motors with a low slip.
An induction motor works with alternating current to create a rotating magnetic field. If you’re wondering whether you’re considered an essential worker during these trying times, check out am i considered an essential worker . The rotating magnetic field in an induction motor interacts with the rotor to produce torque and motion.
Starting Methods
Induction motors can be started using a variety of methods. The most common starting methods are:
- Direct-on-line (DOL) startingis the simplest starting method. It involves connecting the motor directly to the electrical supply. DOL starting is only suitable for small motors.
- Star-delta startingis a reduced-voltage starting method that is used for larger motors. It involves connecting the motor windings in a star configuration during starting and then switching to a delta configuration once the motor has reached a certain speed.
- Autotransformer startingis another reduced-voltage starting method that is used for large motors. It involves using an autotransformer to reduce the voltage applied to the motor during starting.
- Variable-frequency drive (VFD) startingis a sophisticated starting method that provides the most precise control over the starting torque and speed of the motor.
Speed Control
The speed of an induction motor can be controlled using a variety of methods. The most common speed control methods are:
- Variable-frequency drive (VFD) controlis the most versatile speed control method. It involves using a VFD to vary the frequency of the electrical supply to the motor.
- Pole-changingis a method of speed control that involves changing the number of poles in the motor’s stator windings. Pole-changing is a simple and cost-effective method of speed control, but it is only suitable for motors with a limited number of poles.
- Slip-ring controlis a method of speed control that involves adding a slip ring to the rotor of the motor. Slip-ring control provides good speed control, but it is more expensive and complex than other speed control methods.
Applications, An induction motor works with
Induction motors are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Industrial machinery
- Pumps
- Fans
- Compressors
- Conveyors
- Home appliances
Final Thoughts
Our journey into the inner workings of induction motors has reached its end, but the impact of these remarkable machines extends far beyond this discussion. They are the backbone of our technological world, enabling countless innovations and shaping the way we live.
Whether it’s powering our homes, driving our industries, or propelling our vehicles, induction motors continue to play a vital role in our daily lives.
As we leave the realm of induction motors, let’s not forget the principles we’ve learned. The interplay of electricity, magnetism, and motion is a testament to the power of human ingenuity. And who knows, perhaps this newfound knowledge will inspire you to create your own electrifying innovations in the future.
Answers to Common Questions: An Induction Motor Works With
What is the most common type of electrical supply used for induction motors?
Alternating current (AC) is the most common type of electrical supply used for induction motors.
How does the magnetic field interact with the rotor in an induction motor?
The stator’s magnetic field induces an electric current in the rotor, creating a magnetic field of its own. These interacting magnetic fields generate torque, causing the rotor to rotate.
What is the purpose of slip in an induction motor?
Slip is the difference between the synchronous speed of the stator’s magnetic field and the actual speed of the rotor. It allows the motor to develop torque and start under load.