Embark on a fascinating journey into the realm of engines, where we delve into the intricate mechanisms that power our world. From the basics of how an engine works to the diverse types that drive our vehicles, industries, and innovations, we’ll explore the captivating world of these remarkable machines.
Understanding the basics of how an engine works is crucial for anyone interested in engineering. The fundamental principles are similar to those found in an office or post with no work but high pay , where a small input can lead to a significant output.
Just as a piston converts mechanical energy into motion, so too can a well-crafted plan turn minimal effort into substantial rewards. Returning to the topic of engines, understanding their inner workings allows us to appreciate their efficiency and power.
Internal Combustion Engines
An internal combustion engine is a heat engine that converts the chemical energy of a fuel into mechanical energy. The fuel is burned inside the engine, and the expanding gases push a piston, which in turn rotates a crankshaft. Internal combustion engines are used in a wide variety of applications, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and airplanes.
Just like understanding the basics of how an engine works can help you maintain your car, an introduction to the profession of social work 5th edition can equip you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of social work practice.
Both require a solid foundation to build upon, whether you’re troubleshooting an engine or addressing societal challenges.
Four Main Strokes of an Internal Combustion Engine
- Intake stroke: The piston moves down, drawing air and fuel into the cylinder.
- Compression stroke: The piston moves up, compressing the air and fuel mixture.
- Power stroke: The spark plug ignites the air and fuel mixture, causing it to burn and expand. The expanding gases push the piston down, generating power.
- Exhaust stroke: The piston moves up, pushing the exhaust gases out of the cylinder.
Types of Internal Combustion Engines
- Gasoline engines: Gasoline engines are the most common type of internal combustion engine. They use gasoline as fuel and are typically used in cars, trucks, and motorcycles.
- Diesel engines: Diesel engines use diesel fuel and are typically used in trucks, buses, and heavy equipment.
- Rotary engines: Rotary engines are a type of internal combustion engine that uses a triangular rotor instead of a piston. Rotary engines are more compact and lighter than piston engines, but they are also less efficient.
- DC motors: DC motors use direct current (DC) to create a magnetic field. DC motors are simple to control and can provide high torque at low speeds.
- AC motors: AC motors use alternating current (AC) to create a magnetic field. AC motors are more efficient than DC motors and can operate at higher speeds.
- Brushless motors: Brushless motors are a type of AC motor that does not use brushes to make contact with the rotor. Brushless motors are more efficient and reliable than brushed motors.
- Reciprocating steam engines: Reciprocating steam engines use a piston to convert the thermal energy of steam into mechanical energy.
- Turbine steam engines: Turbine steam engines use a turbine to convert the thermal energy of steam into mechanical energy.
- Gas turbines: Gas turbines use hot gases to drive the turbine. Gas turbines are used in a wide variety of applications, including aircraft, power plants, and gas turbines.
- Steam turbines: Steam turbines use steam to drive the turbine. Steam turbines are used in power plants and marine propulsion.
- Jet engines: Jet engines are a type of gas turbine that uses the exhaust gases from the engine to provide thrust.
- Advantages: Rotary engines are more compact and lighter than piston engines. They also have fewer moving parts, which makes them more reliable.
- Disadvantages: Rotary engines are less efficient than piston engines. They also produce more emissions, and they require more maintenance.
Electric Motors: Basics Of How An Engine Works
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric motors are used in a wide variety of applications, including appliances, power tools, and electric vehicles.
An engine works by mixing fuel and air, then igniting the mixture to create power. This process requires a lubricant, and one common lubricant is an oil-water mixture. This mixture is also effective as an insecticidal spray. An oil-water mixture works as an insecticidal spray because it suffocates insects.
When the mixture is sprayed on an insect, it coats the insect’s body and prevents it from breathing. This eventually leads to the insect’s death. The mixture is also effective against a wide range of insects, including aphids, mites, and thrips.
It is a safe and effective way to control pests in your home or garden.
Basic Principles of an Electric Motor
Electric motors work by using the principle of electromagnetism. When an electric current flows through a coil of wire, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of a permanent magnet, causing the coil to rotate.
To understand the basics of how an engine works, we need to delve into the combustion process and the role of pistons, cylinders, and valves. But if you’re looking to broaden your horizons, why not explore the possibility of working in Canada? Check out this resource: apply for an open work permit canada . Returning to our engine discussion, the exhaust system plays a crucial role in expelling combustion gases, ensuring efficient engine operation.
Types of Electric Motors
Steam Engines
A steam engine is a heat engine that converts the thermal energy of steam into mechanical energy. Steam engines were the first type of heat engine to be widely used, and they played a major role in the Industrial Revolution.
The basics of how an engine works involve understanding the combustion process, which converts chemical energy into mechanical energy. Just like an organisation that does community work relies on the collective efforts of its members to achieve its goals, an engine depends on the coordinated operation of its components to generate power.
Understanding these principles helps us appreciate the complexity and efficiency of modern engines.
Basic Principles of a Steam Engine
Steam engines work by using the principle of thermal expansion. When water is heated, it turns into steam. Steam is a gas, and it expands when it is heated. The expanding steam pushes a piston, which in turn rotates a crankshaft.
Just like how an engine’s pistons work tirelessly to power a vehicle, recognizing and appreciating an employee’s hard work is crucial for maintaining a productive and motivated workforce. As we delve into the intricacies of how an engine functions, it’s essential to remember the importance of acknowledging and rewarding those who contribute significantly to the organization’s success.
Appreciating an employee for hard work not only boosts morale but also fosters a culture of excellence, ensuring that the engine of productivity continues to run smoothly.
Types of Steam Engines
Turbine Engines
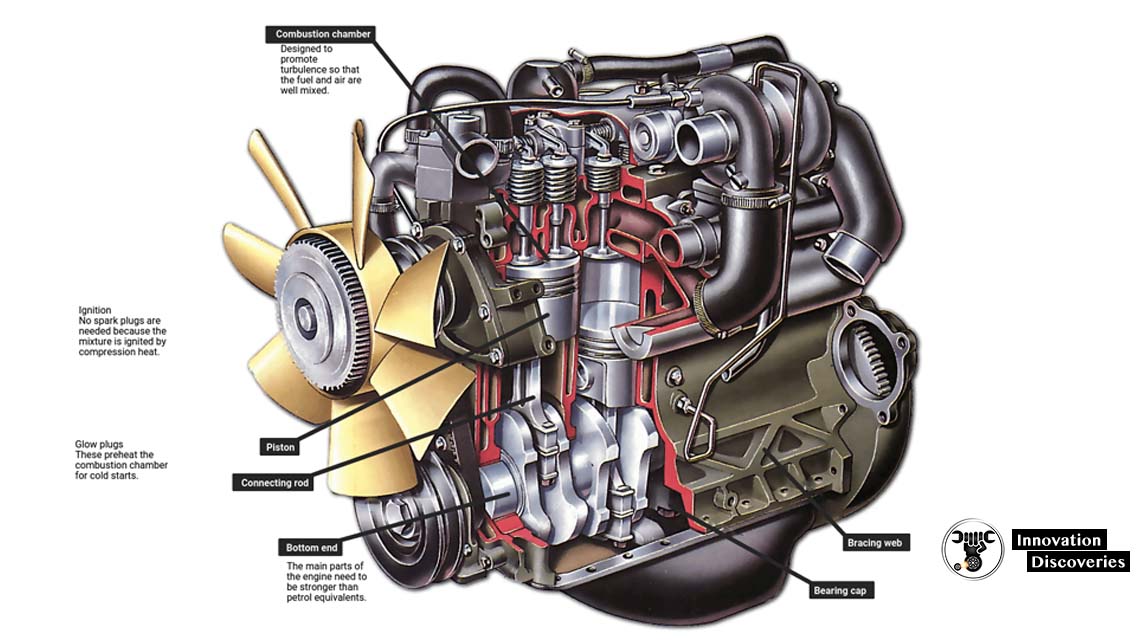
A turbine engine is a heat engine that uses a turbine to convert the thermal energy of a gas into mechanical energy. Turbine engines are used in a wide variety of applications, including aircraft, power plants, and gas turbines.
So, about the basics of how an engine works… The pistons move up and down inside the cylinders, compressing the air-fuel mixture. When the spark plug ignites the mixture, it creates a small explosion that drives the pistons back down.
This up-and-down motion of the pistons turns the crankshaft, which then drives the wheels. It’s a bit like the story of an office worker reincarnated into another world who suddenly has to learn the basics of magic and swordsmanship. Just like that office worker, we’re learning the basics of how an engine works, one step at a time.
Basic Principles of a Turbine Engine
Turbine engines work by using the principle of fluid dynamics. When a gas flows through a turbine, it causes the turbine to rotate. The rotating turbine is connected to a crankshaft, which converts the rotational energy of the turbine into mechanical energy.
Types of Turbine Engines, Basics of how an engine works
Rotary Engines
A rotary engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses a triangular rotor instead of a piston. Rotary engines are more compact and lighter than piston engines, but they are also less efficient.
Basic Principles of a Rotary Engine
Rotary engines work by using the principle of trochoidal motion. The rotor is mounted on an eccentric shaft, and it rotates inside a trochoidal chamber. The trochoidal chamber is shaped like a figure-eight, and it causes the rotor to move in a circular motion.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rotary Engines
Last Word
As we conclude our exploration of engines, we’ve gained a deeper understanding of their fundamental principles, diverse applications, and the intricate symphony of components that orchestrate their operation. May this newfound knowledge ignite your curiosity and inspire you to delve further into the captivating world of engineering.
FAQ Resource
What are the four main strokes of an internal combustion engine?
Intake, compression, power, and exhaust
How do electric motors differ from internal combustion engines?
Electric motors rely on electricity to generate motion, while internal combustion engines burn fuel to create power.
What is the primary advantage of a rotary engine?
Compact size and smooth operation due to its unique triangular rotor design.
Understanding the basics of how an engine works can help you troubleshoot issues with your car. Just like how an post mobile data not working can be caused by a variety of factors, an engine problem can stem from fuel, ignition, or mechanical issues.
By learning the basics of engine operation, you can narrow down the possible causes and get your car back on the road.