An example of a business trade off – In the realm of business, decisions often involve weighing the pros and cons, a delicate dance known as trade-offs. Join us as we delve into an example that showcases the complexities and strategies behind this balancing act.
Definition of Business Trade-Offs
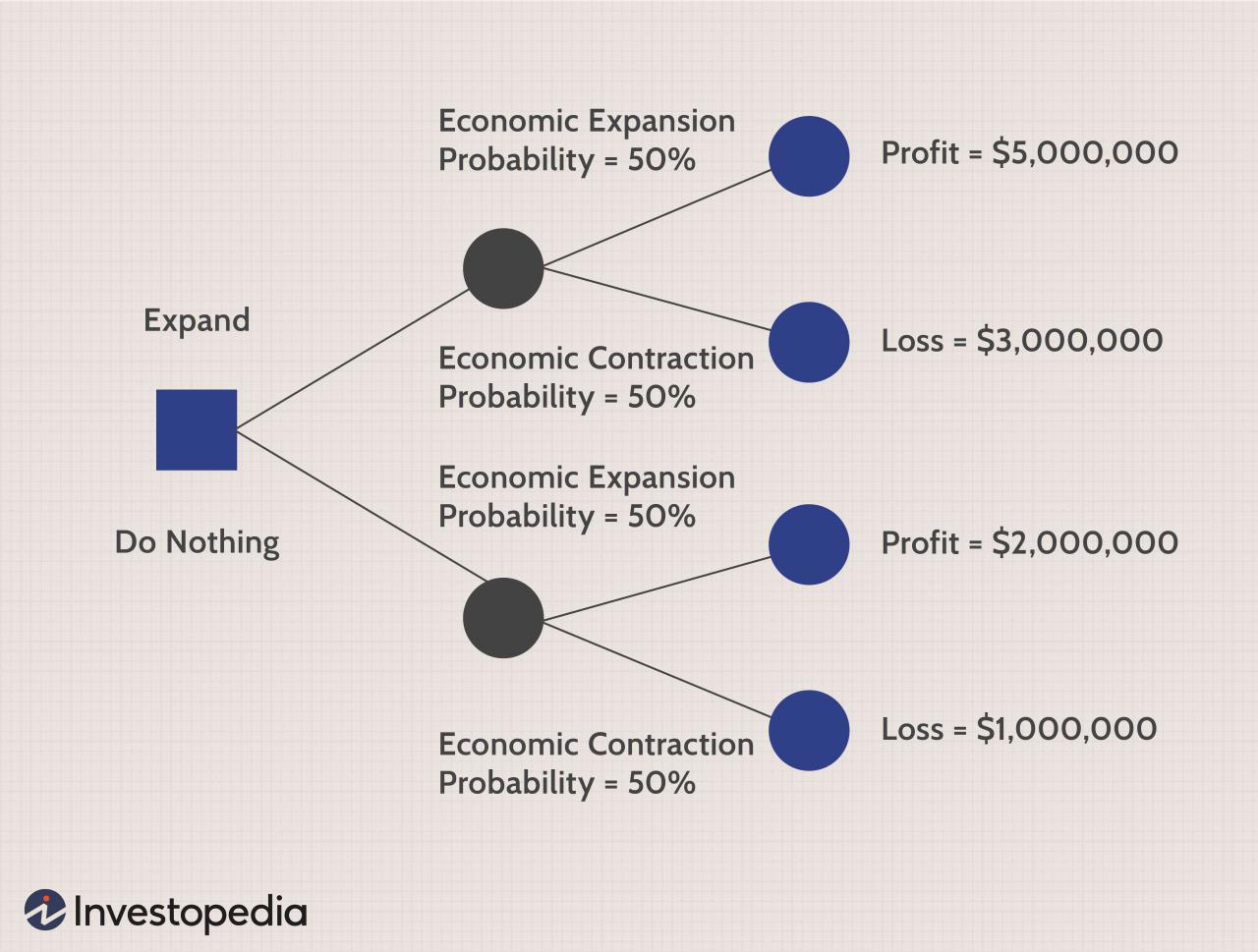
In business, a trade-off is a situation where a company must choose between two or more desirable options, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Trade-offs are a common part of business decision-making. Every decision a company makes involves some kind of trade-off. For example, a company may choose to invest in new equipment to increase production, but this will require the company to give up some of its cash on hand.
Or, a company may choose to hire more employees to improve customer service, but this will increase the company’s labor costs.
Types of Business Trade-Offs
There are many different types of trade-offs that businesses face. Some of the most common include:
- Quality vs. cost:Businesses must often choose between producing high-quality products or services at a higher cost, or producing lower-quality products or services at a lower cost.
- Speed vs. accuracy:Businesses must often choose between making decisions quickly or making decisions that are more accurate.
- Growth vs. profitability:Businesses must often choose between growing their business rapidly or focusing on profitability.
- Innovation vs. stability:Businesses must often choose between investing in new products or services or sticking with the status quo.
Common Examples of Business Trade-Offs
In the world of business, trade-offs are a constant reality. Every decision involves weighing the benefits of one option against the costs of another. Some of the most common trade-offs businesses face include:
Product Quality vs. Cost
- A business may choose to use lower-quality materials to reduce production costs, but this could lead to decreased customer satisfaction and lower sales.
- Alternatively, a business may invest in higher-quality materials to improve product durability, but this could increase production costs and make the product less affordable for customers.
Customer Service vs. Efficiency
- A business may provide excellent customer service by offering a wide range of support options and resolving customer issues quickly. However, this can be expensive and time-consuming.
- On the other hand, a business may prioritize efficiency by limiting customer support options and automating processes. This can reduce costs, but it could also lead to decreased customer satisfaction.
Innovation vs. Stability
- A business may invest in research and development to create new products and services, but this can be risky and expensive.
- Alternatively, a business may focus on maintaining the status quo and avoiding major changes. This can be less risky, but it could also limit growth opportunities.
Methods for Analyzing Business Trade-Offs
Identifying potential trade-offs is crucial in business decision-making. It involves understanding the various options available, their potential consequences, and the relationships between them. A thorough analysis of trade-offs enables businesses to make informed choices that align with their goals and objectives.To
evaluate the potential costs and benefits of different options, businesses can use various techniques such as cost-benefit analysis, scenario planning, and sensitivity analysis. These methods help quantify the financial and non-financial implications of each option, allowing decision-makers to compare and contrast them objectively.
Prioritizing Trade-Offs
Once the potential costs and benefits have been evaluated, businesses need to prioritize trade-offs based on their strategic objectives and risk tolerance. Prioritization techniques include:
- Weighted scoring model:Assigns weights to different criteria and evaluates options based on their performance against those criteria.
- Decision matrix:Compares options based on multiple criteria and ranks them according to their overall desirability.
- Risk assessment:Identifies and evaluates the potential risks associated with each option and determines their likelihood and impact.
Strategies for Making Trade-Off Decisions
In the business world, trade-offs are an inevitable part of decision-making. By understanding the strategies involved in making trade-off decisions, businesses can ensure they are making the best choices possible, even in the face of difficult choices.
There are a number of different strategies that businesses can use to make trade-off decisions. Some of the most common include:
- Cost-benefit analysis:This involves weighing the costs and benefits of each option and choosing the option that provides the greatest net benefit.
- Multi-criteria decision analysis:This involves considering multiple criteria when making a decision, such as financial impact, customer satisfaction, and environmental impact.
- Satisficing:This involves choosing the first option that meets a certain minimum threshold of acceptability, rather than trying to find the perfect option.
Role of Stakeholders in Trade-Off Decision-Making
When making trade-off decisions, it is important to consider the interests of all stakeholders. Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the outcome of a decision. They can include employees, customers, shareholders, suppliers, and the community.
Involving stakeholders in the decision-making process can help to ensure that all perspectives are considered and that the decision is made in a fair and transparent manner.
Communicating Trade-Off Decisions Effectively
Once a trade-off decision has been made, it is important to communicate it effectively to all stakeholders. This will help to ensure that everyone understands the rationale for the decision and that they are on board with the outcome.
There are a number of different ways to communicate trade-off decisions, such as:
- Written reports:These can provide a detailed overview of the decision-making process and the rationale for the decision.
- Presentations:These can be used to present the decision to a larger audience in a more engaging way.
- Meetings:These can be used to discuss the decision with stakeholders and answer any questions they may have.
Impact of Business Trade-Offs on Business Performance

Business trade-offs can significantly impact various aspects of business performance. Positive consequences may include increased profitability, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced employee morale. For instance, a company that prioritizes cost reduction through automation may increase its profit margins. On the other hand, negative consequences can arise when trade-offs are poorly managed.
In the business world, it’s all about trade-offs. You can’t have everything, so you have to decide what’s most important to you. For example, if you want to launch a new product quickly, you may have to sacrifice some quality.
Or, if you want to offer the lowest prices, you may have to cut back on customer service. The same is true for video chatting on Snapchat with an Android . If you want to use all the features of Snapchat, you’ll need to use an iPhone.
But if you’re willing to sacrifice some features, you can use Snapchat on an Android phone.
For example, sacrificing quality to reduce costs may lead to decreased customer satisfaction and reputational damage.
Impact on Profitability
Trade-offs can directly affect a company’s profitability. Prioritizing cost-cutting measures can improve profit margins in the short term, but it may also lead to reduced quality or innovation, ultimately harming long-term profitability. Conversely, investing in research and development may reduce current profits but drive future growth and increased revenue.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
Trade-offs can also impact customer satisfaction. For instance, reducing product features to lower costs may lead to dissatisfied customers who seek alternatives. On the other hand, investing in customer service and support can enhance customer satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and repeat business.
When making business decisions, trade-offs are often necessary. For instance, increasing production might boost revenue but could also raise costs. Similarly, when addressing a business email to an unknown recipient ( addressing a business email to an unknown recipient ), choosing a formal salutation may convey respect but could come across as impersonal.
Ultimately, understanding the potential trade-offs involved in business decisions is crucial for making informed choices.
Impact on Employee Morale
Trade-offs can influence employee morale. Prioritizing cost-cutting measures through layoffs or wage freezes may demoralize employees and lead to decreased productivity. Conversely, investing in employee training and development can boost morale and enhance job satisfaction, resulting in increased productivity and retention.
Case Study
Consider the case of “ABC Company,” which faced a trade-off between expanding its product line and reducing costs. Expanding the product line would increase revenue but require significant investment. Reducing costs would improve profitability but limit growth opportunities. After careful analysis, ABC Company opted to expand its product line, believing that the potential revenue growth outweighed the costs.
Take the example of a business that must decide between using child labor or not. Using child labor could lead to lower production costs, but it also raises moral concerns. Businesses must consider the application of moral standards to business situations and weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks before making a decision.
This decision resulted in increased sales and profitability in the long run.
Ethical Considerations in Business Trade-Offs
Balancing business interests with social and environmental responsibilities is a complex task. Business trade-offs often involve ethical considerations, as decisions can have significant impacts on stakeholders, society, and the environment. It is essential to approach trade-off decisions with a thoughtful and ethical mindset.
Ethical Implications of Trade-Off Decisions
Ethical implications arise when trade-off decisions involve potential harm or benefit to individuals, groups, or the environment. For instance, a company may face a choice between using cheaper materials that have environmental impacts or investing in more sustainable but expensive options.
Such decisions require careful consideration of the ethical consequences and the potential impact on stakeholders.
Balancing Business Interests with Social and Environmental Responsibilities
Businesses have a responsibility to consider the social and environmental impact of their decisions. Balancing business interests with these responsibilities requires a holistic approach. Companies should strive to find solutions that minimize negative impacts and maximize positive contributions to society and the environment.
This may involve investing in sustainable practices, supporting local communities, and promoting ethical business practices.
Examples of Ethical Dilemmas Related to Trade-Offs
Ethical dilemmas arise when there is no clear-cut solution to a trade-off decision. For example, a company may face a choice between laying off employees to reduce costs or continuing to operate at a loss. Such decisions require careful weighing of ethical considerations, such as the impact on employees, the community, and the company’s reputation.
Tools for Analyzing Business Trade-Offs
Analyzing business trade-offs is crucial for making informed decisions that balance multiple objectives. Various tools and techniques can assist in this process, each with its own advantages and limitations.
Choosing the appropriate tool depends on the complexity of the trade-off, the availability of data, and the decision-maker’s preferences.
Decision Matrices
Decision matrices, also known as Pugh matrices, are simple and effective tools for comparing multiple options based on a set of criteria. Each option is evaluated on a scale, and the results are tabulated to identify the best choice.
Advantages:Easy to use, provides a structured framework for comparison.
Limitations:Can be subjective, may not capture all relevant factors.
Cost-Benefit Analyses
Cost-benefit analyses quantify the costs and benefits associated with different options. The option with the highest net benefit (benefits minus costs) is typically the preferred choice.
Advantages:Provides a financial perspective, helps justify decisions.
Limitations:Can be time-consuming, may not capture all intangible factors.
Weighted Scoring Models
Weighted scoring models assign weights to different criteria based on their importance. Each option is then evaluated on each criterion, and the weighted scores are summed to determine the best choice.
Advantages:Allows for customization, provides a quantitative basis for decision-making.
For example, a business might choose to invest in new equipment to increase production, but this could come at the cost of higher operating expenses. This trade-off is a key component in an equilibrium model of the business cycle , which attempts to explain the fluctuations in economic activity over time.
By understanding these trade-offs, businesses can make informed decisions that balance short-term gains with long-term sustainability.
Limitations:Requires accurate weighting of criteria, can be complex to use.
Best Practices for Managing Business Trade-Offs
Effective management of business trade-offs requires a structured and thoughtful approach. Here are some best practices to consider:
Prioritize Objectives: Clearly define the most important business objectives and align trade-off decisions with those priorities.
Involve Stakeholders
Engage key stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors, in the decision-making process to gather diverse perspectives and ensure buy-in.
Quantify and Analyze
Use data and analysis to quantify the potential impact of trade-offs on various business metrics, such as profitability, customer satisfaction, and employee morale.
Consider Long-Term Effects, An example of a business trade off
Evaluate the potential long-term consequences of trade-off decisions to avoid unintended negative outcomes in the future.
Communicate Clearly
Effectively communicate the rationale behind trade-off decisions to stakeholders to foster understanding and support.
When it comes to business trade offs, one example is the choice between investing in new technology or hiring more staff. However, with the advancement of technology, there are now ways to automate tasks that were once done by humans, like taking screenshots on an android.
Check out can you take screenshots on an android to learn how. This can free up staff time to focus on more strategic initiatives, potentially leading to increased productivity and profitability.
Monitor and Adjust
Continuously monitor the impact of trade-off decisions and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal outcomes.
Examples of Successful Trade-Off Management Strategies
Apple’s decision to prioritize user experience over cost in product design has led to sustained customer loyalty and market dominance.
Amazon’s trade-off between low prices and fast delivery has enabled it to become a leader in e-commerce.
For instance, a business may decide to lower prices to increase market share, but this could lead to lower profit margins. A business unit, which refers to an organization that operates as a distinct entity within a larger organization, may face similar trade-offs.
By focusing on specific markets or products, a business unit can increase its efficiency and profitability, but it may also limit its overall growth potential.
Case Studies of Business Trade-Offs
Case studies are an effective way to analyze business trade-offs and learn from the experiences of others. They provide real-world examples of how businesses have navigated trade-offs and the outcomes of their decisions.
Case Study Template
To conduct a case study of a business trade-off, consider the following template:
- Company:Identify the company involved in the case study.
- Trade-off:Describe the trade-off that the company faced.
- Decision-making process:Explain how the company made the decision, including the factors considered and the process followed.
- Outcomes:Discuss the outcomes of the decision, both positive and negative.
- Lessons learned:Identify any lessons that can be learned from the case study.
Case Study Example
Company:Apple Trade-off:Apple faced a trade-off between innovation and cost when developing the iPhone. Decision-making process:Apple decided to prioritize innovation over cost, investing heavily in research and development. Outcomes:The iPhone became a huge success, revolutionizing the smartphone industry. However, it also came with a high price tag.
Lessons learned:Apple’s case study demonstrates the importance of balancing innovation and cost when making business decisions.
Illustrations of Business Trade-Offs
Business trade-offs are a common occurrence in the business world. They involve making decisions that balance two or more competing objectives. Here are a few illustrations of business trade-offs:
Quality vs. Cost
An example of a business trade-off is when a company decides to invest in a new product that has the potential to be successful, but also carries the risk of failure. The company must weigh the potential benefits of the new product against the potential costs.
Similarly, in Android Studio, cannot create an instance of an abstract class error occurs when trying to instantiate an abstract class. This error reminds us of the trade-off between flexibility and efficiency in software development, where abstract classes provide flexibility but cannot be directly instantiated.
- A company may choose to produce a high-quality product at a higher cost or a lower-quality product at a lower cost.
- The trade-off here is between the cost of production and the quality of the product.
Speed vs. Accuracy
- A company may choose to produce a product quickly but with less accuracy or slowly but with greater accuracy.
- The trade-off here is between the speed of production and the accuracy of the product.
Customer Service vs. Profitability
- A company may choose to provide excellent customer service, which can increase costs, or focus on profitability, which may result in lower customer satisfaction.
- The trade-off here is between the cost of providing customer service and the potential for increased revenue from satisfied customers.
Innovation vs. Stability
- A company may choose to invest in innovation, which can lead to new products and services, or focus on stability, which may reduce the risk of failure.
- The trade-off here is between the potential for growth and the risk of failure.
These are just a few examples of the many trade-offs that businesses face. Understanding the trade-offs involved in a decision can help businesses make better choices and achieve their goals.
Resources for Further Learning
Expand your knowledge of business trade-offs with these valuable resources:
Books:
- The Art of Business Trade-Offs: Making Smart Decisions in the Real Worldby Michael J. Mauboussin
- Business Trade-Offs: A Practical Guide to Making Smart Decisionsby Jonathan Knee
- Trade-Offs: Making Smart Decisions When There Are No Easy Answersby Adam Grant
Articles:
- The Art of Business Trade-Offs by Michael J. Mauboussin
- Trade-Offs: A Practical Guide to Making Smart Decisions by Jonathan Knee
- The Science of Trade-Offs by Adam Grant
Websites:
Online Courses:
Ultimate Conclusion: An Example Of A Business Trade Off
Navigating business trade-offs requires careful consideration, a blend of logic and intuition. By understanding the different types, analyzing potential impacts, and employing effective decision-making techniques, businesses can strike a harmonious balance that drives success.
FAQ Overview
What are the key types of business trade-offs?
Businesses commonly face trade-offs between quality and cost, customer service and efficiency, and innovation and stability.
How do businesses analyze trade-offs?
Analysis involves identifying potential trade-offs, evaluating costs and benefits, and prioritizing options based on strategic objectives.
What factors influence trade-off decisions?
Stakeholders, market conditions, financial constraints, and ethical considerations all play a role in shaping trade-off decisions.