A business unit refers to an organization that operates as a distinct entity within a larger company. These units are responsible for specific products, services, or geographic regions and play a crucial role in driving the overall success of the organization.
Business units are designed to enhance operational efficiency, foster innovation, and align with the strategic objectives of the parent company. By understanding the concept and functions of business units, organizations can optimize their structure and performance.
Definition of Business Unit: A Business Unit Refers To An Organization That
A business unit is a self-contained division or segment of an organization that operates independently and is responsible for its own profit and loss. It typically has its own management team, resources, and customers. Business units allow large organizations to manage their operations more effectively and efficiently by decentralizing decision-making and accountability.
Examples of Business Units
Examples of business units within an organization include:
Product divisions
A business unit refers to an organization that operates as a distinct entity within a larger organization. For example, Apple and Samsung are both business units that produce and sell smartphones. Can you track an Apple Tag with an Android phone ? That depends on the specific model of Android phone you have.
A business unit refers to an organization that is responsible for its own financial performance and has its own management team.
These units are responsible for developing, manufacturing, and marketing specific products or product lines. For example, a technology company may have separate business units for its hardware, software, and services divisions.
A business unit refers to an organization that focuses on a specific product or service line. For instance, if you’re wondering can you hide an app on android phone , the answer is yes, but it depends on the phone model and Android version.
Coming back to the topic, a business unit may have its own marketing, sales, and operations functions, allowing it to operate independently within the larger organization.
Geographic divisions
A business unit refers to an organization that operates as a distinct entity within a larger organization. These units are responsible for specific products, services, or geographical regions. Just like how Snapchat has different business units for its various features, like the one for video chat.
Can you video chat on Snapchat with an Android ? The answer is yes, you can! Snapchat’s video chat feature is available on both iOS and Android devices. A business unit refers to an organization that focuses on specific goals and objectives, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency.
These units are responsible for managing the organization’s operations in specific geographic regions. For example, a retail company may have separate business units for its North American, European, and Asian operations.
Functional divisions
These units are responsible for performing specific functions across the organization. For example, a manufacturing company may have separate business units for its production, sales, and marketing functions.
A business unit refers to an organization that is responsible for a specific set of products or services. For example, a business unit might be responsible for all of the company’s sales in a particular region. Do you know can you connect an android to a tv ? A business unit can also be responsible for a specific product line, such as all of the company’s computers.
Organizational Structure
Business units are fundamental components within the organizational structure of a company. They are designed to operate as semi-autonomous entities, each responsible for a specific product line, service, or geographic region. This structure allows for greater flexibility and responsiveness to market changes.
Within business units, reporting relationships and lines of authority are clearly defined. Typically, the head of the business unit reports directly to the CEO or a senior executive. The business unit head has the authority to make decisions regarding the unit’s operations, including product development, marketing, sales, and finance.
Reporting Relationships
- Business unit heads report directly to the CEO or a senior executive.
- Business unit heads have the authority to make decisions regarding their unit’s operations.
- Reporting relationships are clearly defined within business units.
Lines of Authority
- Business unit heads have the authority to make decisions regarding their unit’s operations.
- Lines of authority are clearly defined within business units.
- Reporting relationships and lines of authority are essential for effective decision-making and coordination within the organization.
Business Unit Functions
Business units are responsible for carrying out specific functions that contribute to the overall success of the organization. These functions typically align with the core competencies and strategic objectives of the business unit and may vary depending on the industry and nature of the organization.
A business unit refers to an organization that operates independently within a larger company. If you’re wondering, can you charge a juul with an android charger , the answer is yes. However, it’s important to note that using an Android charger may not provide the optimal charging experience for your JUUL device.
A business unit refers to an organization that may have its own management team, employees, and resources.
Some of the key functions commonly performed by business units include:
Product Development and Innovation
- Conducting market research and analysis to identify customer needs and trends
- Developing and launching new products or services
- Managing product lifecycles and ensuring continuous improvement
Sales and Marketing
- Developing and executing marketing strategies to promote products and services
- Managing sales channels and customer relationships
- Generating leads and closing deals
Operations and Production
- Managing production processes and ensuring efficient operations
- Optimizing supply chain management and inventory control
- Maintaining quality standards and ensuring compliance with regulations
Finance and Accounting
- Managing financial resources and preparing financial statements
- Analyzing financial performance and making investment decisions
- Ensuring compliance with accounting and tax regulations
Human Resources
- Recruiting, hiring, and developing employees
- Managing employee benefits and compensation
- Ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations
Information Technology
- Developing and maintaining IT infrastructure and systems
- Providing technical support and troubleshooting
- Ensuring data security and compliance with regulations
Business Unit Goals and Objectives
The process of setting goals and objectives for business units is crucial for aligning their activities with the overall strategic objectives of the organization. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
To set effective goals, business unit leaders must first understand the organization’s strategic plan and identify how their unit can contribute to its achievement. They should then develop goals that are aligned with the organization’s overall mission, vision, and values.
A business unit refers to an organization that specializes in a particular area or industry. For instance, you might be wondering if you can you skype with an android . The answer is yes, you can Skype with an Android device.
In fact, there are several different ways to do so. A business unit refers to an organization that focuses on a specific product or service.
Alignment with Organizational Objectives
Business unit goals should be closely aligned with the overall strategic objectives of the organization. This ensures that the unit’s activities are contributing to the achievement of the organization’s long-term goals. For example, if an organization has a strategic objective to increase market share, a business unit might set a goal to increase sales by 10% in the next year.
By aligning business unit goals with organizational objectives, organizations can ensure that all parts of the organization are working towards the same common goal. This can help to improve coordination and collaboration, and it can also help to prevent duplication of effort.
Business Unit Performance Measurement
Evaluating the performance of business units is crucial for assessing their effectiveness and making informed decisions. Various methods and metrics are employed to measure unit performance.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics are essential in quantifying unit performance. These include financial metrics like revenue, profit, and return on investment (ROI), as well as operational metrics such as customer satisfaction, market share, and employee productivity.
Financial Metrics
- Revenue: Total income generated from sales or services.
- Profit: Net income after deducting expenses from revenue.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measure of financial return on investment in the unit.
Operational Metrics
- Customer Satisfaction: Level of satisfaction among customers with products or services.
- Market Share: Percentage of total market controlled by the unit.
- Employee Productivity: Output or efficiency of employees within the unit.
Business Unit Autonomy and Accountability
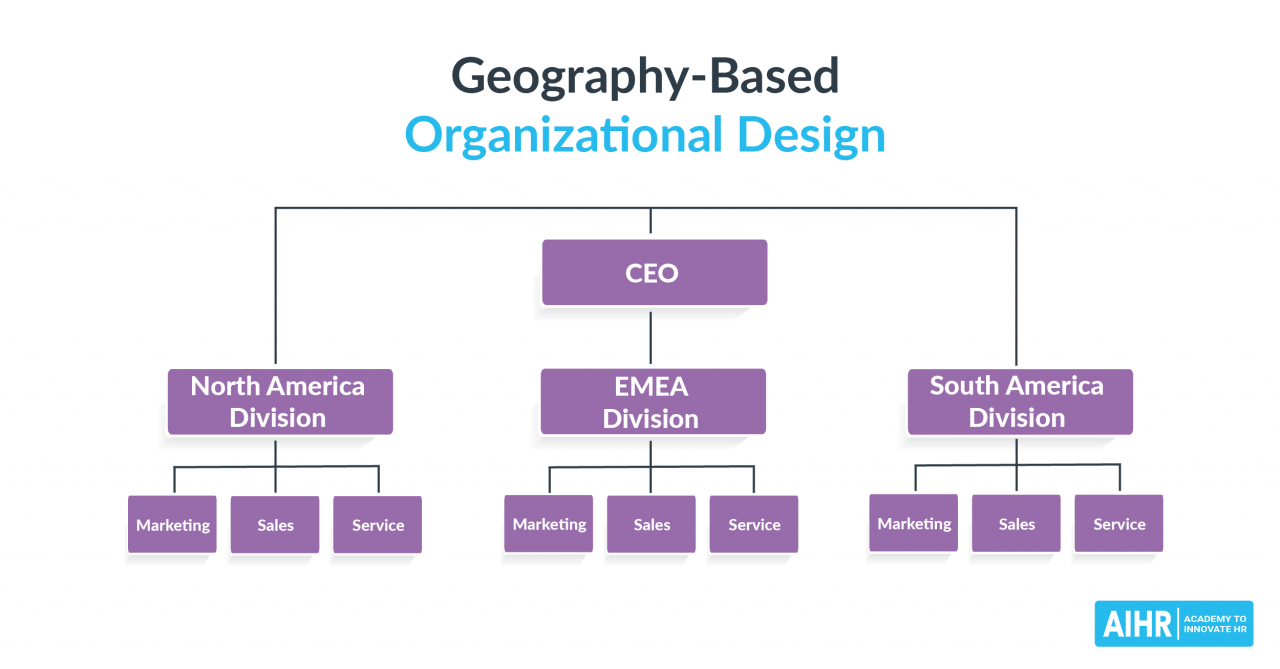
Business units often operate with varying degrees of autonomy, allowing them to make decisions and manage their operations independently. This autonomy empowers unit leaders to respond swiftly to market changes and pursue growth opportunities.
Concurrently, business unit leaders are held accountable for their unit’s performance. They are responsible for achieving financial targets, meeting customer expectations, and driving operational efficiency. This accountability ensures alignment with the organization’s overall goals and objectives.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Units
The advantages and disadvantages of organizing a company into business units are multifaceted and interdependent. By understanding these factors, organizations can make informed decisions about the best organizational structure for their specific needs and goals.
Advantages of Business Units
- Improved Focus and Specialization:Business units allow companies to focus on specific products, markets, or customer segments. This specialization can lead to improved efficiency and effectiveness, as employees can develop deep expertise in their respective areas.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Responsiveness:Business units can respond more quickly to changing market conditions than a centralized organization. This flexibility allows companies to adapt to new opportunities and threats more effectively.
- Increased Profitability:Business units can be held accountable for their own financial performance. This accountability can motivate employees to improve efficiency and profitability.
- Improved Decision-Making:Business units can make decisions more quickly and efficiently than a centralized organization. This can lead to faster time-to-market and a competitive advantage.
- Increased Innovation:Business units can encourage innovation by providing employees with the freedom to experiment and take risks.
Disadvantages of Business Units
- Potential for Conflict and Duplication:Business units can sometimes compete with each other for resources and customers. This can lead to conflict and duplication of effort.
- Increased Complexity:Managing a company with multiple business units can be more complex than managing a centralized organization. This complexity can lead to higher costs and inefficiencies.
- Loss of Centralized Control:Business units can have a degree of autonomy, which can lead to a loss of centralized control. This can make it difficult to implement company-wide policies and strategies.
- Increased Coordination Costs:Coordinating activities between multiple business units can be time-consuming and costly. This can reduce the overall efficiency of the organization.
Case Studies of Business Units
Various business units have achieved remarkable success, demonstrating the effectiveness of this organizational structure. Let’s explore a few notable case studies and analyze the key factors that contributed to their triumphs.
A business unit refers to an organization that is a distinct entity within a larger organization. For example, a business unit might be a division, a subsidiary, or a branch. A business unit typically has its own management team, its own financial statements, and its own strategic plan.
For instance, you may wonder can you skype with an android phone . That’s a separate concern from a business unit’s goals, but still relevant to the daily operations of a business unit.
GE Healthcare
- Customer Focus:GE Healthcare prioritized understanding and fulfilling customer needs, resulting in innovative medical solutions.
- Operational Efficiency:Lean Six Sigma practices optimized operations, reducing costs and improving productivity.
- Innovation:A dedicated focus on research and development led to groundbreaking medical technologies.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- First-Mover Advantage:AWS pioneered cloud computing, establishing itself as an industry leader.
- Scalability:AWS’s infrastructure enabled businesses to scale their operations seamlessly.
- Customer Service:Excellent customer support and technical assistance enhanced customer satisfaction.
Emerging Trends in Business Unit Management
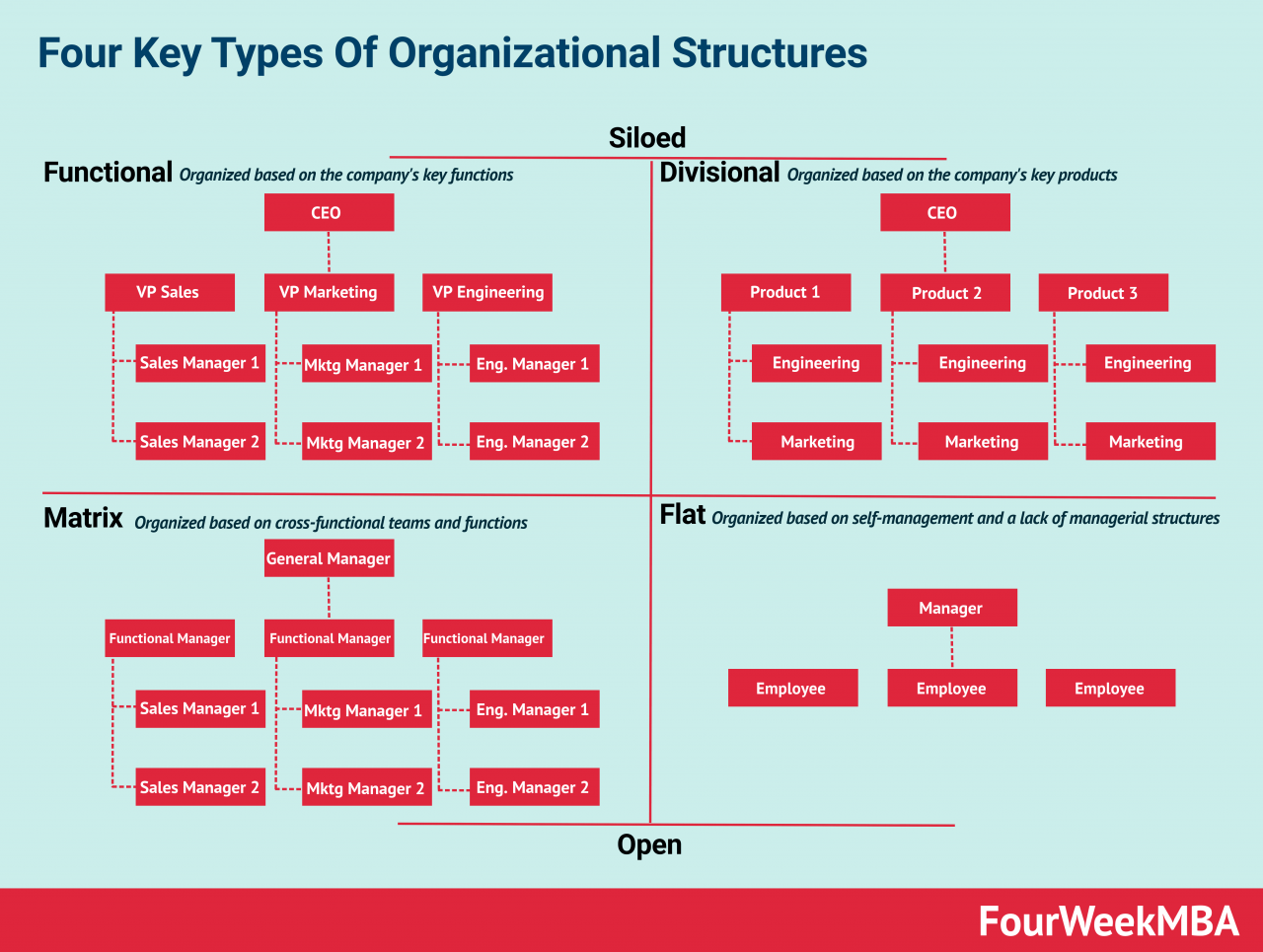
Business unit management is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by the emergence of new technologies and the increasing availability of data. These trends are reshaping the role and responsibilities of business units, and are creating new opportunities for organizations to improve their performance.
One of the most significant trends in business unit management is the increasing use of technology. Technology can be used to automate tasks, improve communication and collaboration, and provide real-time data on business performance. This information can help business unit managers make better decisions, identify opportunities for improvement, and respond more quickly to changes in the market.
Data Analytics
Another major trend in business unit management is the increasing use of data analytics. Data analytics can be used to identify patterns and trends in data, and to develop predictive models that can help businesses make better decisions. For example, data analytics can be used to identify customers who are at risk of churn, or to develop new products and services that are likely to be successful.
These trends are having a significant impact on the role and responsibilities of business unit managers. Business unit managers are now expected to be more technologically savvy and to have a strong understanding of data analytics. They also need to be able to make decisions quickly and to be able to adapt to change.
Best Practices for Business Unit Management
Effective business unit management is crucial for the success of an organization. It requires a well-structured organizational design, robust performance management systems, and focused leadership development initiatives.
Organizational Design, A business unit refers to an organization that
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities within business units.
- Establish clear reporting lines and communication channels.
- Ensure alignment between business unit goals and overall organizational objectives.
Performance Management
Implement performance management systems that:
- Set clear performance targets and metrics.
- Provide regular feedback and coaching to employees.
- Reward and recognize exceptional performance.
Leadership Development
Invest in leadership development programs that:
- Identify and develop high-potential leaders.
- Provide opportunities for mentorship and training.
- Foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, business units are essential components of modern organizations, enabling companies to operate effectively and efficiently. By understanding the functions, goals, and performance measurement of business units, organizations can leverage their potential to drive growth, innovation, and overall success.
General Inquiries
What is the primary purpose of a business unit?
Business units are established to enhance operational efficiency, foster innovation, and align with the strategic objectives of the parent company.
How are business units typically structured within an organization?
Business units can be structured based on product lines, geographic regions, or customer segments, depending on the nature of the organization and its operations.
What are some key functions performed by business units?
Business units typically handle functions such as product development, marketing, sales, customer service, and financial management.