An example of a sole proprietorship business is a captivating tale of individual enterprise and the pursuit of entrepreneurial dreams. Dive into the world of sole proprietorships, where one person takes the reins and embarks on a journey of self-reliance and boundless potential.
From the joys of being your own boss to the challenges of managing it all, we’ll explore the ins and outs of sole proprietorships, providing you with a comprehensive guide to this exciting business structure.
Definition of Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is a form of business owned and operated by a single individual. It is the most basic and common form of business organization. In a sole proprietorship, the owner is personally liable for all debts and obligations of the business.
This means that if the business fails, the owner’s personal assets can be used to pay off the business’s debts.
Key Characteristics of a Sole Proprietorship
The key characteristics of a sole proprietorship are as follows:
- Owned and operated by a single individual
- The owner is personally liable for all debts and obligations of the business
- The business is not a separate legal entity from the owner
- The owner has complete control over the business
- The business is relatively easy to establish and operate
Advantages of Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorship offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for entrepreneurs and small business owners. These benefits include:
Full Control
As a sole proprietor, you have complete control over all aspects of your business. You make all the decisions, set your own hours, and manage your finances. This level of autonomy allows you to tailor your business to your specific needs and goals.
Flexibility
Sole proprietorships are highly flexible, allowing you to adapt quickly to changing market conditions or customer demands. You can easily adjust your product or service offerings, pricing, or marketing strategies without the need for approval from others.
Low Start-Up Costs
Compared to other business structures, sole proprietorships have relatively low start-up costs. You don’t need to file for incorporation or pay franchise fees, and you can often operate your business from your home.
Tax Benefits
Sole proprietorships can take advantage of certain tax benefits, such as the ability to deduct business expenses from your personal income taxes. This can help reduce your overall tax liability.
Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
Operating a sole proprietorship comes with certain drawbacks and risks that entrepreneurs should carefully consider. These disadvantages include:
- Unlimited Liability:As a sole proprietor, you are personally liable for all debts and obligations of your business. This means that if your business is sued, your personal assets (such as your home, car, and savings) can be at risk.
- Limited Access to Capital:Sole proprietorships often have limited access to capital compared to other business structures. This can make it difficult to grow your business or invest in new opportunities.
- Lack of Employee Benefits:As a sole proprietor, you are not eligible for employee benefits such as health insurance, paid time off, or retirement contributions.
- Tax Implications:Sole proprietorships are taxed as individuals, which can result in higher tax rates than other business structures.
- Time Commitment:Running a sole proprietorship requires a significant time commitment. You will be responsible for all aspects of your business, from marketing and sales to customer service and accounting.
Examples of Sole Proprietorship Businesses
Sole proprietorships can be found in various industries, ranging from retail to consulting to construction. Here are a few real-world examples of successful sole proprietorship businesses:
Freelance Writing:Many writers operate as sole proprietors, offering their services to clients in need of content creation, copywriting, or editing. They generate revenue by charging per project or hour worked.
Consulting
Consultants provide expert advice and guidance to businesses and individuals. They specialize in a particular area, such as marketing, finance, or human resources. Sole proprietor consultants typically charge hourly rates or project fees.
For instance, if you’re running a small business like a coffee shop as a sole proprietor, you might need to write a formal business letter to a supplier to order coffee beans. This letter would include your business name, address, and contact information, as well as the date, the supplier’s name and address, and the details of your order.
Home-Based Businesses
Many sole proprietors operate home-based businesses, such as online stores, handmade crafts, or pet grooming services. They generate revenue through online sales, direct sales, or appointments.
Photography
Photographers often operate as sole proprietors, offering their services for events, portraits, or commercial projects. They generate revenue by charging session fees or selling prints and digital images.
One example of a sole proprietorship business is a freelance writer who works from home. This type of business is owned and operated by one person, and the owner is personally liable for all debts and obligations of the business.
If you’re a sole proprietor, it’s important to keep track of your business expenses and income, as you’ll be responsible for paying taxes on your business profits. Also, have you ever wondered can you unsend an android text ? As a sole proprietor, you’ll need to be organized and efficient in order to succeed.
Landscaping
Landscapers provide lawn care, gardening, and other outdoor services to residential and commercial clients. They generate revenue by charging hourly rates or project fees.
Legal Considerations for Sole Proprietorships
Starting a sole proprietorship involves certain legal requirements that ensure your business operates within the law and protects your interests. Understanding these requirements is crucial for a successful and compliant business operation.
One example of a sole proprietorship business is a freelance writer. They have the flexibility to set their own hours and work from anywhere, which are just a couple of the advantages of an entrepreneur starting a business . As a sole proprietor, they are responsible for all aspects of their business, from marketing and sales to customer service and accounting.
However, they also have the potential to earn a higher income than they would as an employee.
Registering your business with the relevant government agencies is essential. This process varies depending on your location, but typically involves filing paperwork with the county clerk or state agency. Registration provides legal recognition to your business and allows you to open business accounts and obtain necessary licenses.
Obtaining Necessary Licenses
Depending on the nature of your business, you may need to obtain specific licenses or permits. These licenses ensure that your business meets industry standards and regulations. For example, if you operate a food-related business, you will likely need a food handling license.
Research the specific requirements for your industry and obtain the necessary licenses to avoid legal penalties and maintain compliance.
For instance, a sole proprietorship, where one person owns and operates a business, can be considered agile. An agile business often adapts quickly to changing market demands and customer needs, just like a sole proprietorship that can make decisions and implement changes swiftly due to its streamlined structure.
Tax Implications of Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorships are taxed as pass-through entities, meaning that the business’s income and expenses are reported on the owner’s personal tax return. This can be advantageous for businesses that have low profits, as it allows them to avoid paying corporate income taxes.
However, it can also be disadvantageous for businesses that have high profits, as the owner will be taxed on all of the business’s income, even if they do not withdraw it from the business.
Tax Deductions and Credits Available to Sole Proprietors
Sole proprietors are eligible for a number of tax deductions and credits that can help to reduce their tax liability. These include:
- Business expenses:Sole proprietors can deduct the ordinary and necessary expenses of running their business, such as rent, utilities, supplies, and travel expenses.
- Depreciation and amortization:Sole proprietors can depreciate or amortize the cost of certain assets, such as equipment and vehicles, over a period of time.
- Health insurance premiums:Sole proprietors who are self-employed can deduct the cost of their health insurance premiums.
- Retirement contributions:Sole proprietors can make tax-deductible contributions to a retirement account, such as an IRA or 401(k).
- Child and dependent care expenses:Sole proprietors who have children or other dependents can deduct the cost of child care or dependent care expenses.
Management and Operations of a Sole Proprietorship
Effectively managing and operating a sole proprietorship requires a comprehensive approach encompassing various aspects. From marketing and customer service to financial management, strategic planning is crucial for success. This section provides guidance on these key areas to help sole proprietors navigate the complexities of running their businesses.
For instance, a freelance writer who runs their own business is an example of a sole proprietorship. However, if you’re wondering whether your business is considered essential during this time, you can check out the guidelines provided by the government here . As a sole proprietor, it’s crucial to stay informed about such matters to ensure your business can continue operating smoothly.
Marketing Strategies
- Develop a clear target market definition to focus marketing efforts effectively.
- Utilize a mix of online and offline marketing channels to reach potential customers.
- Create compelling marketing content that highlights the unique value proposition of the business.
- Track and analyze marketing campaigns to optimize results and maximize ROI.
Customer Service
- Provide exceptional customer service to build strong relationships and foster loyalty.
- Establish clear communication channels and respond promptly to customer inquiries.
- Handle complaints and feedback professionally to maintain a positive brand image.
li>Go the extra mile to exceed customer expectations and create a memorable experience.
Financial Management
- Maintain accurate financial records to track income, expenses, and profits.
- Create a budget to allocate resources effectively and control spending.
- Explore financing options, such as loans or lines of credit, to support business growth.
- Consult with a financial advisor to optimize financial strategies and minimize tax liability.
Financing Options for Sole Proprietorships
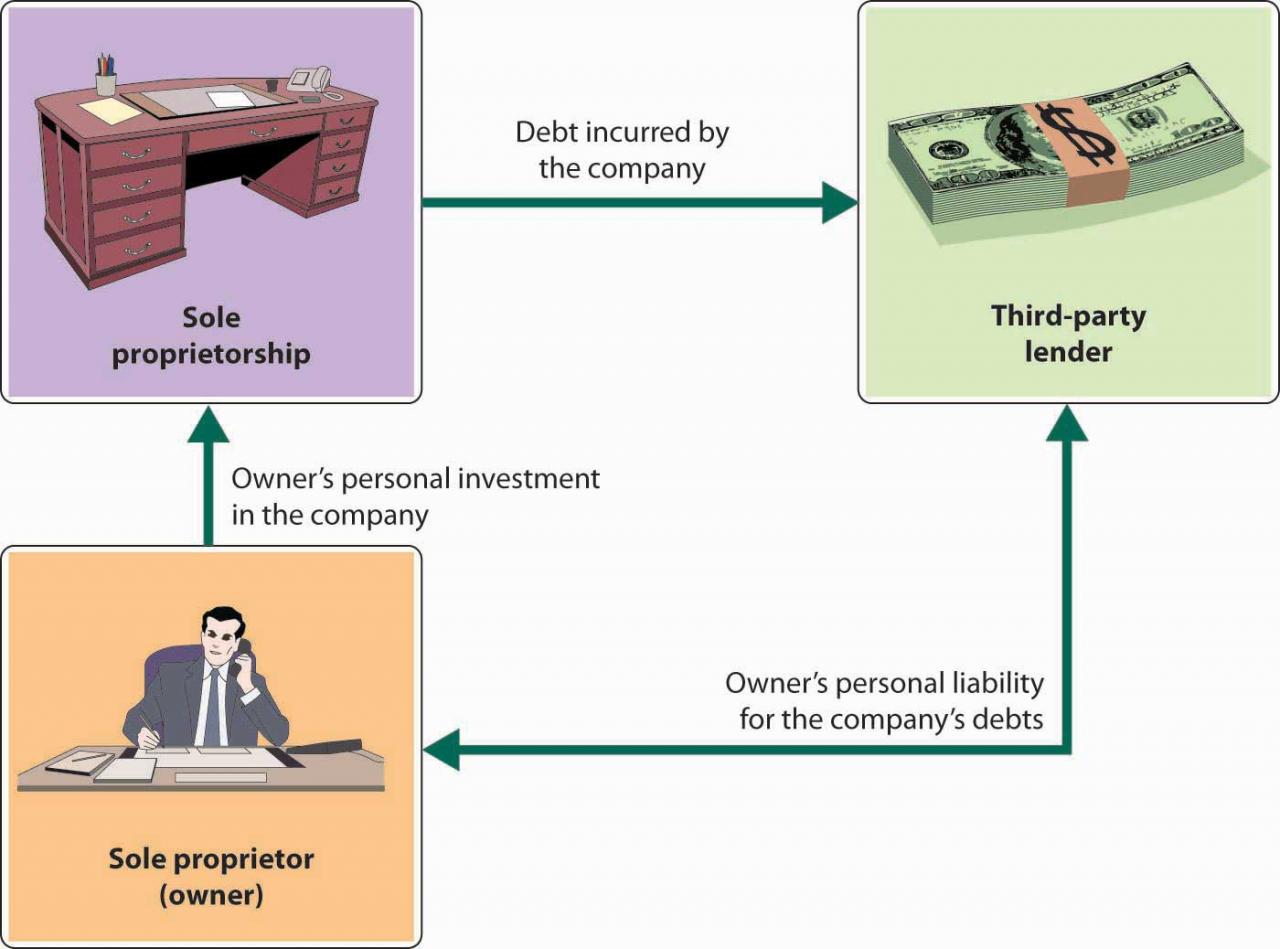
Financing a sole proprietorship can be challenging, but there are several options available to help business owners get the capital they need. These options include:
Business Loans
Business loans are one of the most common financing options for sole proprietors. These loans can be used for a variety of purposes, such as purchasing inventory, expanding operations, or hiring new employees. Business loans are typically repaid over a period of several years, and interest rates can vary depending on the lender and the creditworthiness of the borrower.
Lines of Credit
Lines of credit are another popular financing option for sole proprietors. These lines of credit allow business owners to borrow money as needed, up to a certain limit. Lines of credit are typically revolving, meaning that the borrower can repay the borrowed funds and then borrow again, as long as they stay within the credit limit.
Credit Cards
Credit cards can be a convenient way to finance small business expenses. However, credit cards typically have high interest rates, so it is important to use them wisely. Business owners should only use credit cards for short-term financing needs, such as purchasing supplies or covering unexpected expenses.
Venture Capital
Venture capital is a type of financing that is provided to early-stage businesses with high growth potential. Venture capitalists typically invest in businesses that have the potential to generate large returns on investment. In exchange for their investment, venture capitalists typically receive an equity stake in the business.
A classic example of a sole proprietorship is a freelance writer who works from home. They have the freedom to set their own hours and choose their own projects. However, they also have to deal with the downside of being self-employed, such as having to find their own clients and manage their own finances.
This is just an example of a business trade off that all business owners have to make. In the case of a sole proprietorship, the trade-off is between the freedom and flexibility of being your own boss and the responsibility and risk that comes with it.
Angel Investors
Angel investors are individuals who invest their own money in early-stage businesses. Angel investors typically invest in businesses that they believe have the potential to be successful. In exchange for their investment, angel investors typically receive an equity stake in the business.
Let’s think about an example of a sole proprietorship business. It’s a small business owned by one person, like a local coffee shop or a freelance writer. These businesses have a unique perspective on ethical issues, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Check out an ethical perspective of business csr and the covid-19 pandemic for more insights. Sole proprietorships have a personal stake in their business, so they’re often driven by a sense of responsibility to their customers and community.
Growth and Expansion of Sole Proprietorships: An Example Of A Sole Proprietorship Business
Sole proprietorships can experience growth and expansion by implementing various strategies. These include increasing revenue streams, hiring employees, and expanding into new markets.
Increasing Revenue
Proprietors can increase revenue by offering additional products or services, upselling existing customers, or exploring new pricing strategies. For instance, a freelance writer could offer editing services in addition to writing, or a home baker could introduce catering services to supplement their baked goods sales.
Hiring Employees, An example of a sole proprietorship business
As the business grows, proprietors may need to hire employees to handle the increased workload. This allows the proprietor to focus on strategic planning and business development while delegating tasks to a capable team. However, hiring employees brings additional responsibilities, such as payroll management and employee benefits.
Expanding into New Markets
Sole proprietorships can expand their reach by entering new markets, whether geographically or through online platforms. For example, a local coffee shop could open a second location in a neighboring town, or an Etsy seller could expand their product line to Amazon.
Market research and understanding customer needs are crucial for successful expansion.
Concluding Remarks
The example of a sole proprietorship business serves as a testament to the power of individual initiative and the rewards that come with taking ownership of your work. Whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur or simply curious about the world of business, this exploration into sole proprietorships will leave you inspired and equipped with valuable insights.
Common Queries
What is the key characteristic of a sole proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is a business owned and operated by a single individual, who has complete control over its operations and assumes all financial and legal responsibilities.
What are the advantages of a sole proprietorship?
Sole proprietorships offer flexibility, ease of setup, and full control over decision-making.
What are the disadvantages of a sole proprietorship?
Sole proprietors have unlimited personal liability, meaning they are personally responsible for any debts or obligations incurred by the business.