Can an Exempt Employee Refuse to Work Overtime?
Can an exempt employee refuse to work overtime – Exempt employees are not entitled to overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). However, they may still be required to work overtime by their employers. In this article, we will discuss the statutory framework governing overtime for exempt employees, the employer’s obligations, the employee’s rights, practical considerations, and relevant case law and precedent.
Can an exempt employee refuse to work overtime? In some jurisdictions, such as Ontario, employees may have the right to refuse overtime work under certain circumstances. For more information on the specific laws and regulations governing overtime work in Ontario, please refer to the following resource: Can an Employee Refuse to Work Overtime in Ontario.
It is important for both employers and employees to be aware of their rights and obligations regarding overtime work to ensure compliance with applicable laws and maintain a fair and equitable work environment.
1. Statutory Framework
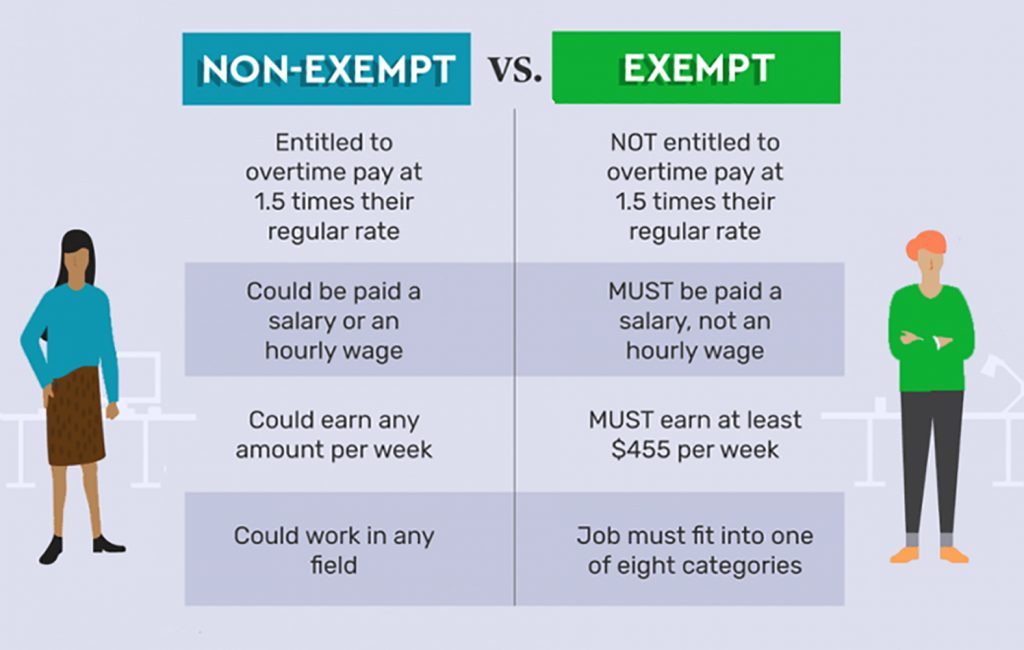
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) is the primary federal law governing overtime pay for non-exempt employees. However, the FLSA does not apply to exempt employees. Exempt employees are those who meet certain criteria, such as being paid on a salary basis and performing certain types of duties.
While an exempt employee can generally refuse to work overtime without repercussions, there are certain exceptions to this rule. For instance, an employee may be required to work overtime in order to complete a project that is essential to the company’s operations.
In addition, an employee may volunteer to work without pay, even if they are exempt from overtime pay. Can an employee volunteer to work without pay ? Yes, an employee can volunteer to work without pay, even if they are exempt from overtime pay.
However, the employee must be clear that they are not working overtime and that they are not expecting to be paid for their time. Exempt employees who refuse to work overtime without pay may be subject to disciplinary action.
The concept of “bona fide” overtime is important in the context of exempt employees. Bona fide overtime is overtime work that is not performed by an exempt employee as part of their regular job duties. If an exempt employee is required to work bona fide overtime, they are entitled to overtime pay.
Can an exempt employee refuse to work overtime? In some cases, yes. However, chemical engineers working in oil companies may have different considerations due to the nature of their work. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to work overtime depends on the specific circumstances and the employee’s contract.
2. Employer Obligations
Employers have the right to require overtime work from exempt employees. However, there are some limitations on this right. For example, employers cannot require exempt employees to work overtime if it would violate the employee’s health or safety.
Exempt employees are generally not required to work overtime, but there are some exceptions. For example, an employer may require an exempt employee to work overtime in an emergency situation. However, an exempt employee can refuse to work overtime if they have a valid reason, such as a family emergency or a religious obligation.
If an employer retaliates against an exempt employee for refusing to work overtime, the employee may be able to file a complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). Can an employer force you to return to work ? The answer is generally no, but there are some exceptions.
For example, an employer may be able to require you to return to work if you are a healthcare worker or if you are needed to respond to an emergency. However, an employer cannot force you to work overtime if you are an exempt employee.
Employers are not required to compensate exempt employees for overtime work. However, some employers may choose to do so as a matter of policy.
In certain situations, an exempt employee may refuse to work overtime. However, if a student nurse is employed as an AIN, they may have different obligations. To learn more about the specific regulations governing student nurses working as AINs, visit here.
Additionally, it’s important to consider the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) when determining an exempt employee’s overtime eligibility.
3. Employee Rights
Exempt employees have the right to refuse overtime work. However, there are some limitations on this right. For example, exempt employees may not be able to refuse overtime work if it is necessary to complete a project or meet a deadline.
If an exempt employee refuses overtime work, they may face consequences, such as being passed over for promotions or being terminated.
4. Practical Considerations
There are a number of practical considerations for employers and employees regarding overtime work for exempt employees. Employers should develop clear policies regarding overtime work and communicate these policies to employees.
Employees should be aware of their rights and responsibilities regarding overtime work. They should also be aware of the potential consequences of refusing overtime work.
5. Case Law and Precedent
There is a body of case law that has addressed the issue of overtime for exempt employees. These cases have helped to shape the legal landscape and provide guidance to employers and employees.
One notable case is Martin v. Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., in which the Supreme Court ruled that employers cannot require exempt employees to work overtime without compensation if the overtime work is not bona fide.
Ending Remarks
Ultimately, the right of exempt employees to refuse overtime work is a delicate balance between employer needs and employee rights. By understanding the legal framework, employer obligations, and employee rights, both parties can navigate this issue effectively, fostering a harmonious and productive work environment.
Essential FAQs
Can an exempt employee be fired for refusing overtime?
In general, no. Exempt employees have the right to refuse overtime work without fear of retaliation or termination.
Are there any exceptions to the right to refuse overtime?
Yes, there may be limited exceptions, such as emergencies or situations where the employee’s refusal would cause undue hardship to the employer.
What should an exempt employee do if they are pressured to work overtime?
Employees should politely but firmly assert their right to refuse overtime work. They should also document any instances of pressure or coercion.
An exempt employee is not required to work overtime, but there are exceptions. For example, a dental hygienist may be required to work overtime in an orthodontics office if there is an emergency. Can a dental hygienist work in an orthodontics office ?
The answer is yes, but it depends on the state in which they are practicing. In some states, dental hygienists are only allowed to work under the supervision of a dentist. However, in other states, dental hygienists are allowed to practice independently.
An exempt employee may refuse to work overtime if it would violate their religious beliefs or if they have a disability that prevents them from doing so. However, some states have laws that allow employers to require overtime work in certain circumstances.
For example, an 18 year old may not be able to work at a dispensary in some states, even if they have a medical marijuana card. In such cases, the employee may be able to request a reasonable accommodation from their employer.
Even exempt employees who are not entitled to overtime pay may still refuse to work overtime in certain circumstances. For example, if an exempt employee is sick, they may be able to refuse to work overtime under the same laws that protect other employees from being forced to work when they are ill.
Can an employer force you to work when sick in Canada ? Learn more about the relevant laws and your rights as an exempt employee.