Business analysis in an agile scrum environment – Embark on a journey through the dynamic world of business analysis in Agile Scrum environments, where we’ll explore the challenges and opportunities that await you. Join us as we unravel the secrets to effective collaboration, communication, and measuring success in this fast-paced, iterative world.
Agile Scrum Environment Overview: Business Analysis In An Agile Scrum Environment
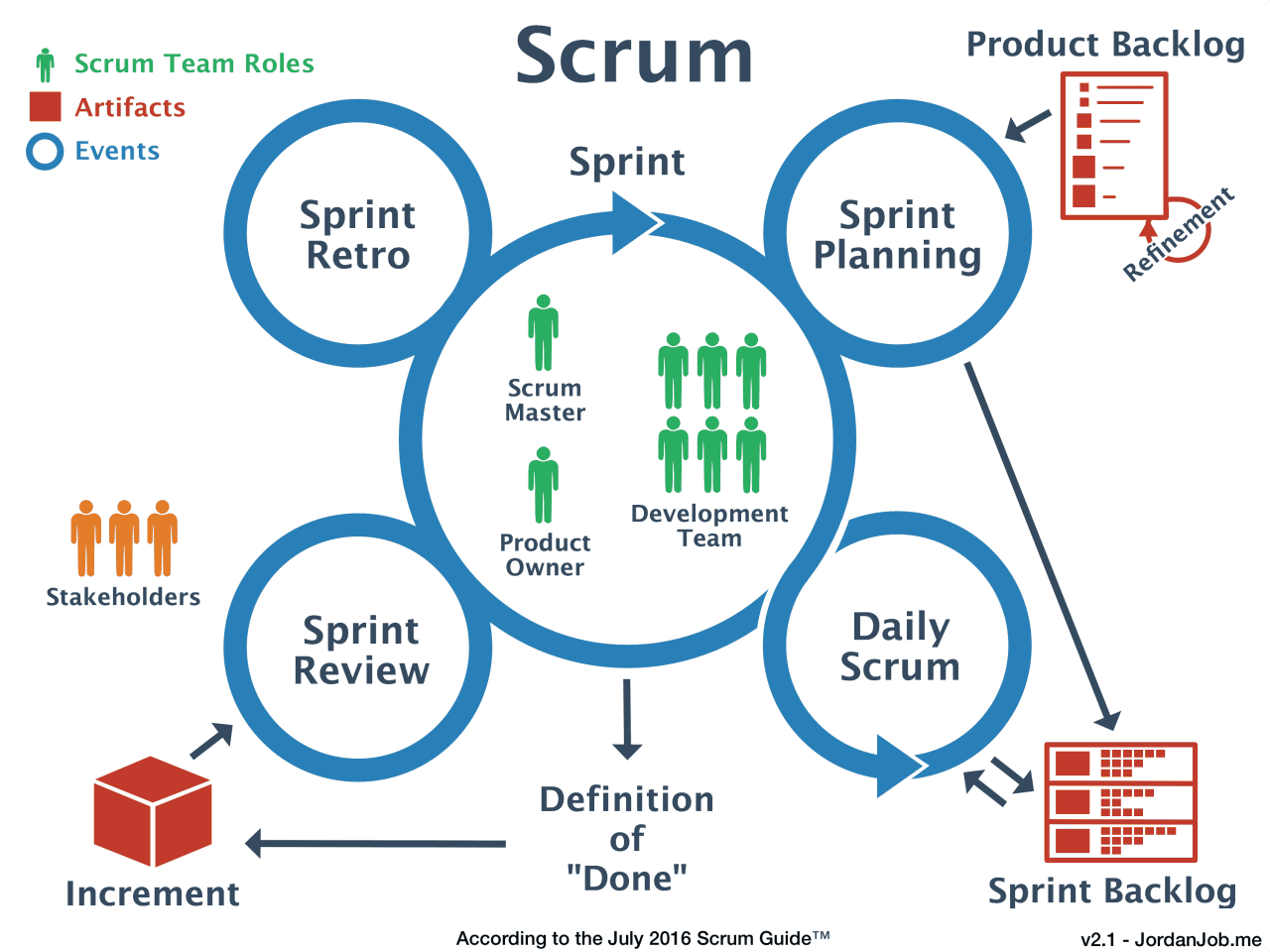
Agile Scrum is a framework for developing software in an iterative and incremental manner. It is based on the principles of agility, which emphasize collaboration, communication, and flexibility.
Business analysis in an agile scrum environment is essential for ensuring the successful delivery of projects. By utilizing tools available with an amazon business account and healthcare license , analysts can streamline their processes and gain valuable insights into project progress.
These tools provide real-time visibility into project status, allowing analysts to identify potential risks and make data-driven decisions to mitigate them, ensuring the project’s success within the agile scrum framework.
The Scrum framework consists of a series of sprints, which are short periods of time (typically two to four weeks) during which a team works to complete a specific set of goals. Sprints are followed by retrospectives, which are meetings where the team reflects on the previous sprint and identifies areas for improvement.
Roles and Responsibilities within a Scrum Team
- Product Owner:The Product Owner is responsible for defining the vision and goals of the product. They also prioritize the requirements and work with the team to ensure that the product meets the needs of the stakeholders.
- Scrum Master:The Scrum Master is responsible for facilitating the Scrum process and removing any impediments that the team may encounter. They also help the team to stay focused and on track.
- Development Team:The Development Team is responsible for developing the product. They work together to complete the tasks that are assigned to them during each sprint.
Business Analysis in Agile Scrum
Business analysts play a critical role in Agile Scrum environments. They are responsible for gathering and analyzing requirements, validating and prioritizing them, and managing change requests.
If you’re just starting out in business analysis in an agile scrum environment, you’ll need a laptop that can keep up with your fast-paced workflow. The best laptop for starting an online business will have a powerful processor, plenty of RAM, and a long battery life.
It should also be lightweight and portable so you can take it with you wherever you go. Once you have the right laptop, you’ll be able to focus on what’s important: delivering high-quality business analysis in an agile scrum environment.
Business analysts also work with the Scrum team to ensure that the product meets the needs of the stakeholders. They provide valuable insights into the business domain and help the team to make informed decisions.
Business analysis in an agile scrum environment requires a keen understanding of the business context and its impact on project outcomes. As an analyst, it’s crucial to consider external factors that may influence the project, such as an increase in business taxes.
An increase in business taxes causes can have a direct impact on the project budget and timelines, as well as the overall financial health of the organization. Therefore, it’s essential to incorporate this knowledge into the analysis to ensure the project’s success and alignment with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Challenges and Opportunities of Business Analysis in Agile Scrum
- Challenges:Business analysts may face challenges in Agile Scrum environments, such as the need to be flexible and adaptable, and the need to work closely with the development team.
- Opportunities:Business analysts also have opportunities in Agile Scrum environments, such as the opportunity to have a greater impact on the product, and the opportunity to learn new skills.
Business Analysis Activities in Agile Scrum
Business analysts perform a variety of activities in Agile Scrum environments, including:
Gathering and Analyzing Requirements
Business analysts gather requirements from stakeholders through a variety of methods, such as interviews, workshops, and surveys. They then analyze the requirements to identify the key features and functionality that the product must have.
In business analysis within an agile scrum environment, it’s crucial to consider how an organization defines its business . This understanding influences how the team prioritizes features, ensures alignment with organizational goals, and ultimately drives successful project outcomes. By defining its business in terms of its mission, vision, and values, the organization provides a clear framework for decision-making and enables the team to deliver solutions that truly meet its strategic objectives.
Validating and Prioritizing Requirements, Business analysis in an agile scrum environment
Business analysts validate requirements with stakeholders to ensure that they are accurate and complete. They also prioritize requirements to help the team to decide which requirements to work on first.
In the realm of business analysis within an agile scrum environment, we delve into the depths of identifying potential business opportunities. By architecting a solution for an identified potential business , we empower organizations to transform their ideas into tangible solutions.
This iterative process, embedded within the agile scrum framework, ensures that business analysis remains a cornerstone of innovation and growth.
Managing Change Requests
Business analysts manage change requests throughout the development process. They work with stakeholders to understand the impact of the change and to determine whether or not the change should be implemented.
Business analysis in an agile scrum environment provides the foundation for successful project outcomes. By breaking down complex requirements into manageable chunks and working iteratively, teams can deliver value incrementally. This approach aligns well with the end-to-end business brainly concept explored by Accenture here . In an agile scrum environment, business analysts play a crucial role in bridging the gap between business needs and technical implementation, ensuring that the delivered solutions meet the desired business outcomes.
Collaboration and Communication
Collaboration and communication are essential in Agile Scrum environments. Business analysts must work closely with the Scrum team to ensure that the product meets the needs of the stakeholders.
Business analysts can collaborate with the Scrum team in a variety of ways, such as by participating in sprint planning meetings, attending daily stand-ups, and reviewing code.
Challenges and Best Practices of Communication in Agile Scrum Environments
- Challenges:Business analysts may face challenges in communicating with the Scrum team, such as the need to use technical language and the need to be able to communicate effectively in a fast-paced environment.
- Best Practices:Business analysts can use a variety of best practices to communicate effectively in Agile Scrum environments, such as using clear and concise language, and being willing to listen to and understand the perspectives of others.
Measuring Success
Measuring the success of business analysis in Agile Scrum environments is important to ensure that the business is getting value from the investment.
Business analysis in an agile scrum environment relies heavily on data analysis and decision-making. For a deeper understanding of these concepts, refer to an overview of business intelligence analytics and decision support . By integrating data-driven insights into agile scrum processes, analysts can enhance project outcomes, prioritize features, and optimize resource allocation.
There are a variety of metrics that can be used to measure the success of business analysis, such as the number of requirements that are gathered, the number of defects that are found, and the number of change requests that are managed.
In an agile scrum environment, business analysis can provide valuable insights for project planning and execution. However, it’s important to consider the potential benefits of purchasing an existing business to streamline operations and reduce risks. By acquiring an established business, organizations can leverage existing infrastructure, customer base, and industry expertise.
This can provide a solid foundation for implementing agile scrum practices and enhancing overall project outcomes.
Challenges and Best Practices of Measuring Success in Agile Scrum Environments
- Challenges:Business analysts may face challenges in measuring the success of business analysis in Agile Scrum environments, such as the need to be able to track and measure the impact of business analysis activities.
- Best Practices:Business analysts can use a variety of best practices to measure the success of business analysis in Agile Scrum environments, such as using a variety of metrics to measure success, and by communicating the results of the measurement to stakeholders.
Closing Notes
As we conclude our exploration of business analysis in Agile Scrum, remember that embracing collaboration, effective communication, and data-driven decision-making are key to unlocking the full potential of this transformative approach. By harnessing these principles, you can drive innovation, deliver value, and achieve exceptional outcomes in your projects.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the key benefits of business analysis in Agile Scrum?
Enhanced stakeholder satisfaction, improved product quality, reduced project risks, and increased agility.
How do business analysts gather requirements in Agile Scrum?
Through user stories, interviews, workshops, and observation.
What are the challenges of measuring success in Agile Scrum environments?
Rapidly changing requirements, lack of traditional metrics, and the need for continuous feedback.